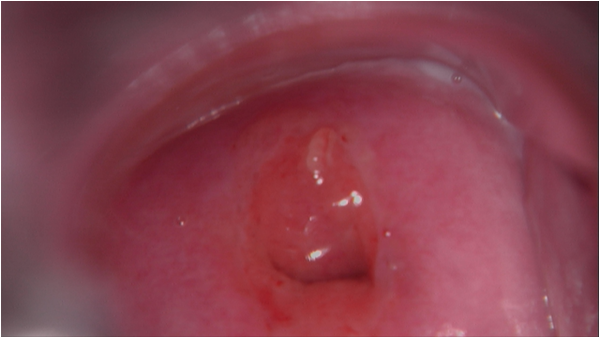
Colposcopy is a medical diagnostic procedure used to closely examine a woman's cervix, vagina,and vulva for signs of disease, particularly after a Pap smear result which reveals abnormal results or if there is suspicion of conditions like cervical cancer, precancerous changes, genital warts, or other abnormalities in the cervical tissue.
Indications for ColposcopyColposcopy is a medical procedure used to closely examine the cervix, vagina, and vulva for signs of disease. Colposcopy helps in early detection and appropriate treatment of cervical issues.
Colposcopy is a procedure used to examine the cervix, vagina, and vulva for signs of disease, usually after an abnormal Pap smear.
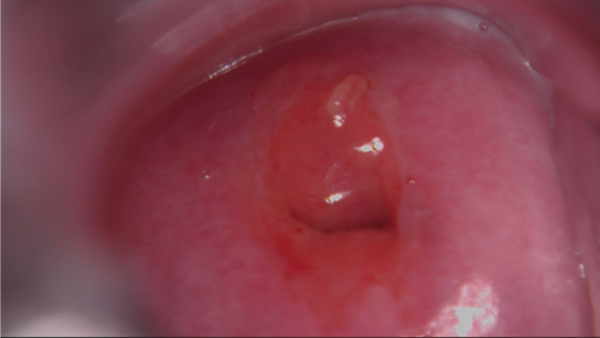

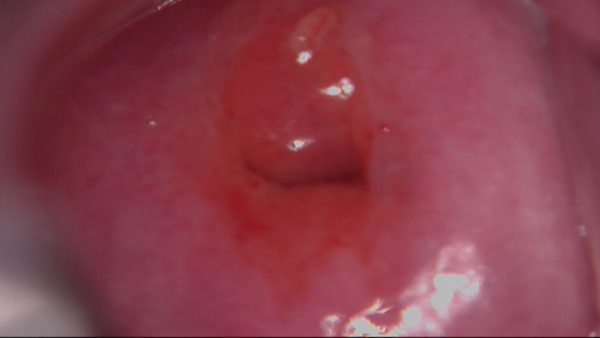
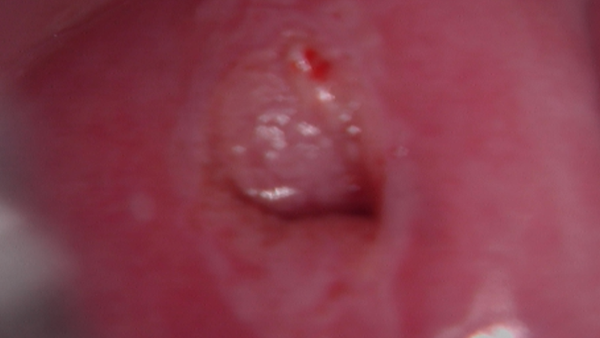
Follow-up : Depending on the results of the colposcopy and biopsy, follow-up may include further tests, treatment, or a repeat colposcopy.
Colposcopy is a safe procedure, but risks may include infection or bleeding, especially if a biopsy is taken. But you should call your Healthcare professional if you observe any of the following symptoms:
Following your doctor's care instructions closely will help ensure proper healing.
Colposcopy is a simple and painless procedure.Colposcopy can help medical professionals detect cancer or cancer cells early, so you can get the treatment you need. Cervical cancer is diagnosed and treated early and can be cured.
A colposcopy can also rule out cancer.Discuss your concerns about cancer and the results with your Healthcare professional as you prepare for the test day.